How do serious workplace injuries impact your business? The OSHA Days Away, Restricted or Transferred (DART) rate is an excellent tool for measuring these recordable incidents' effect on a business over time.
While the DART rate is used by OSHA to follow and assess trends in high-risk industries, EHS managers can use the data from the DART rate to continuously improve their company’s Safety Management System.
What Is OSHA Dart Rating?
DART is the acronym for Days Away, Restricted or Transferred. The DART formula tracks OSHA recordable injuries that result in:
- Time Away from work
- Restricted job roles/tasks
- Permanent transfer to a new position
OSHA includes all of the above when determining which incidents will be included in the DART calculation. Remember, though, if an incident results in a worker being away from work and then returning to work with restricted tasks, there is still only one incident, for the OSHA formula. The DART rate only determines the frequency of these lost time incidents.
The DART rate calculation only takes data from injuries or illnesses that result from an incident at the workplace. Pre-existing conditions or injuries sustained away from the workplace are not included.

What Is The DART Calculation?
The DART rate is calculated using the following formula:
- (Number of OSHA Recordable injuries and illnesses that resulted in Days Away; Restricted; Transferred X 200,000) / Employee hours worked = Days Away Restricted Transferred (DART) Rate
Let’s take a closer look at this formula. Remember, the type of injury recorded in the DART rate is one that results in an employee stopping work in their usual capacity
The 200,000 is the hours worked by 100 employees at 40 hours per week for 50 weeks per year.
So, what kind of DART rate raises red flags for OSHA? When time-away injuries over the year are spread out over 1000 employees working 40 hours a week, the DART rate will not raise cause for concern. When the same number of incidents occur in a smaller company, the red flag starts waving! OSHA may see the DART rate as an indication of a lack of compliance with Health and Safety legislation. That being said, OHSA recognizes that each industry has its own level of risk and includes this factor when assessing a company’s DART rate. When a company has a high DART rate, OSHA takes into account that there are an anticipated number of injuries that will occur in a dangerous work environment. When a business in a low-risk industry, like retail or manufacturing, shows a high DART rate, it is definitely time for the company to put a strong plan in place to correct the problem. However, unless the incident rates for a small company are consistently high over a number of years, OSHA will not usually take enforcement action.
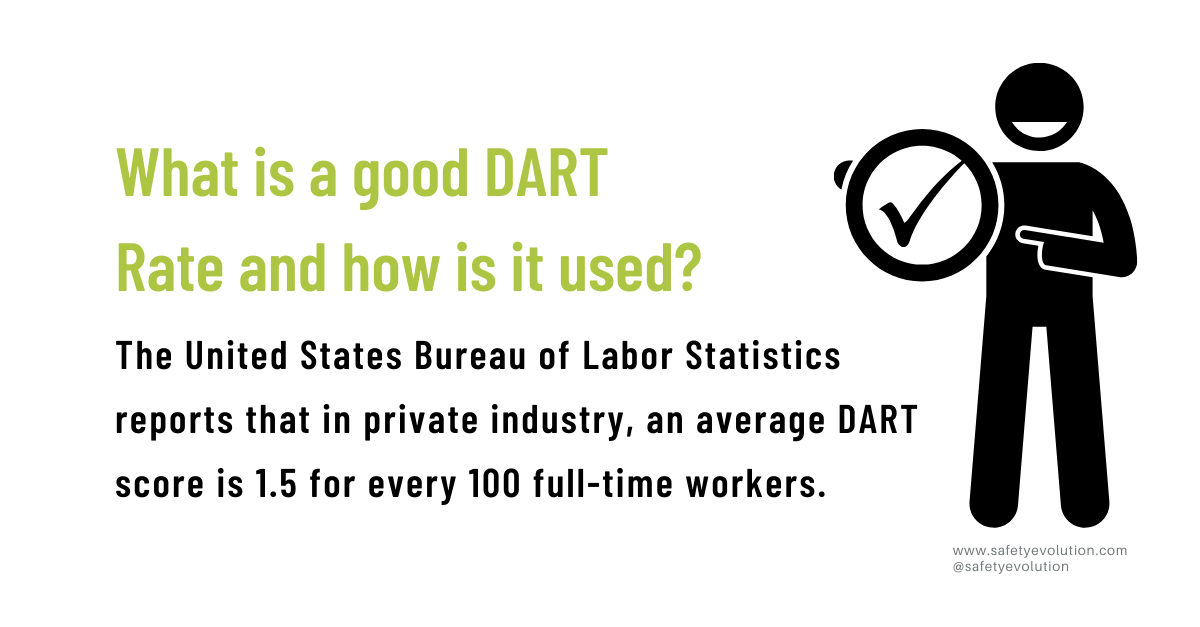
What Is A Good DART Rate And How Is It Used?
The DART Rate is unlike other formulated scores. Yes, the formula is always the same for determining the rate, but with the DART, OSHA considers additional factors and not just the number that the formula produces. Insurance providers also examine the data submitted and base their rates accordingly.
The United States Bureau of Labor Statistics reports that in private industry, an average DART score is 1.5 for every 100 full-time workers.
Like all other safety metrics, the DART rate is a valuable benchmark. Don’t just send your data off to OSHA and leave it at that! Serious incidents need to be taken SERIOUSLY!!
Even though the DART rate is determined by Lagging indicators, both EHS managers and upper-level managers can use their DART rate to compare safety performance year by year. Look for ways to strengthen your company’s safety culture and successfully implement new safety strategies. Lower your DART by preventing serious injuries and illnesses from recurring!

Is it DART or TRIR?
There is often confusion around which data to use for which formula. Ideally, your DART rate will be lower than your TRIR.
Your TRIR or Total Recordable Incident Rate includes all work-related injuries per 100 full-time employees
OSHA defines recordable injury or illness as :
- Any work-related fatality.
- Any work-related injury or illness that results in loss of consciousness, days away from work, restricted work, or transfer to another job.
- Any work-related injury or illness requiring medical treatment beyond first aid.
To read more about TRIR, click on the link below.
How Is TRIR Calculated? Get Your Rating Now With Our TRIR Calculator!
Since the Days Away, Restricted or Transferred Rate deals with serious injury, your DART should be lower than your TRIR. Ensure that your DART data includes only the injuries/illnesses that fit the Days Away, Restricted or Transferred criteria.

How Can Safety Software Help with DART Rate?
Collecting and assessing data can be cumbersome and time-consuming with a paper-based Safety Management System. This is where moving your company to Safety Software will allow you to make huge strides in the evaluation of the success of your system.

STOP WASTING TIME FILING PAPER FORMS - HAVE OUR TEAM DIGITIZE YOUR FORMS FOR FREE.
Subscribe below for more weekly content digging into all things Health and Safety!